In 2020, we will launch our next Mars rover. It will journey more than 33 million miles to the Red Planet where it will land, explore and search for signs of ancient microbial life. But how do we pinpoint the perfect location to complete this science…when we’re a million miles away on Earth?

We utilize data sent to us by spacecraft on and orbiting Mars. That includes spacecraft that have recorded data in the past.
This week, hundreds of scientists and Mars enthusiasts are gathering to deliberate the four remaining options for where we’re going to land the Mars 2020 rover on the Red Planet.
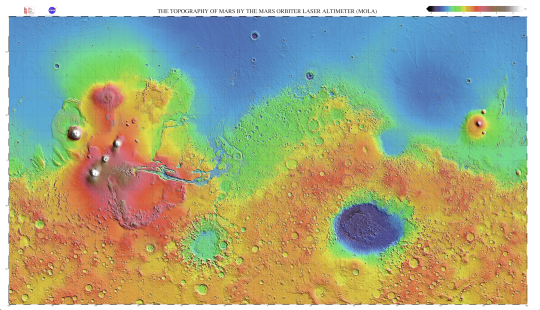
The landing site for Mars 2020 is of great interest to the planetary community because, among the rover’s new science gear for surface exploration, it carries a sample system that will collect rock and soil samples and set them aside in a “cache” on the surface of Mars. A future mission could potentially return these samples to Earth. The next Mars landing, after Mars 2020, could very well be a vehicle which would retrieve these Mars 2020 samples.
Here’s an overview of the potential landing sites for our Mars 2020 rover…
Northeast Syrtis
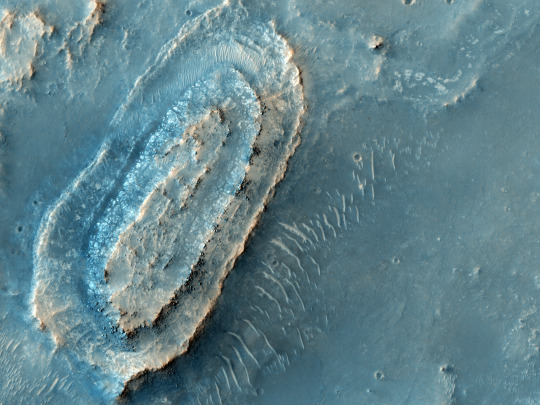

This area was once warmed by volcanic activity. Underground heat sources made hot springs flow and surface ice melt. Microbes could have flourished here in liquid water that was in contact with minerals. The layered terrain there holds a rich record of interactions between water and minerals over successive periods of early Mars history.
Jezero Crater
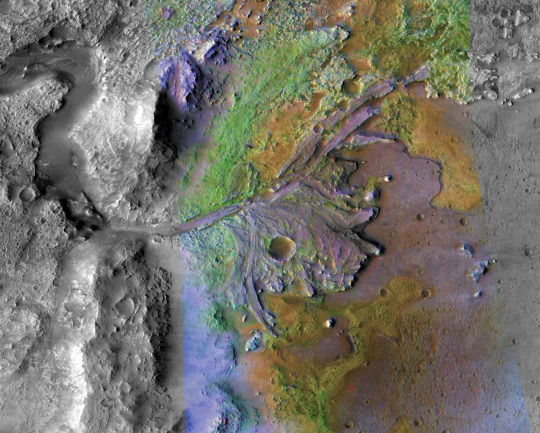

This area tells a story of the on-again, off-again nature of the wet past of Mars. Water filled and drained away from the crater on at least two occasions. More than 3.5 billion years ago, river channels spilled over the crater wall and created a lake. Scientists see evidence that water carried clay minerals from the surrounding area into the crater after the lake dried up. Conceivably, microbial life could have lived in Jezero during one or more of these wet times. If so, signs of their remains might be found in lakebed sediments.
Columbia Hills

At this site, mineral springs once bubbled up from the rocks. The discovery that hot springs flowed here was a major achievement of the Mars Exploration Rover, Spirit. The rover’s discovery was an especially welcome surprise because Spirit had not found signs of water anywhere else in the 100-mile-wide Gusev Crater. After the rover stopped working in 2010, studies of its older data records showed evidence that past floods may have formed a shallow lake in Gusev.
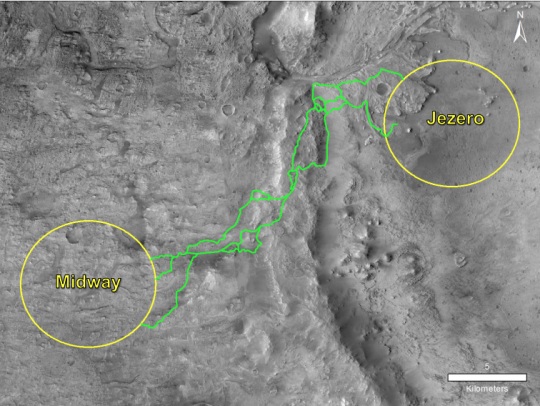
Midway
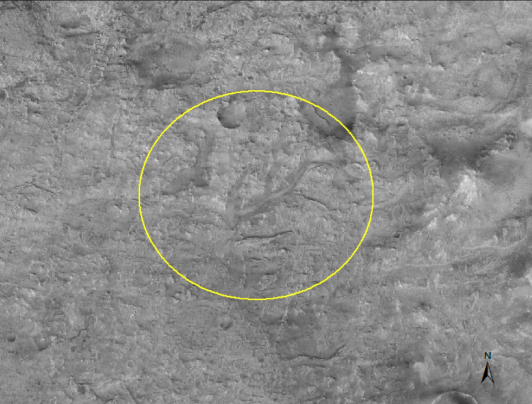

Candidate landing sites Jezero and Northeast Syrtis are approximately 37 km apart…which is close enough for regional geologic similarities to be present, but probably too far for the Mars 2020 rover to travel. This midway point allows exploration of areas of both landing sites.
How Will We Select a Site?
The team is gathered this week for the fourth time to discuss these locations. It’ll be the final workshop in a series designed to ensure we receive the best and most diverse range of information and opinion from the scientific community before deciding where to send our newest rover.
The Mars 2020 mission is tasked with not only seeking signs of ancient habitable conditions on Mars, but also searching for signs of past microbial life itself. So how do we choose a landing site that will optimize these goals? Since InSight is stationary and needs a flat surface to deploy its instruments, we’re basically looking for a flat, parking lot area on Mars to land the spacecraft.
The first workshop started with about 30 candidate landing sites and was narrowed down to eight locations to evaluate further. At the end of the third workshop in February 2017, there were only three sites on the radar as potential landing locations…
…but in the ensuing months, a proposal came forward for a landing site that is in between Jezero and Northeast Syrtis – The Midway site. Since our goal is to get to the right site that provides the maximum science, this fourth site was viewed as worthy of being included in the discussions.
Now, with four sites remaining, champions for each option will take their turn at the podium, presenting and defending their favorite spot on the Red Planet.

On the final day, after all presentations have concluded, workshop participants will weigh the pros and cons of each site. The results of these deliberations will be provided to the Mars 2020 Team, which will incorporate them into a recommendation to NASA Headquarters. A final selection will be made and will likely be announced by the end of the year.
To get more information about the workshop, visit: https://marsnext.jpl.nasa.gov/workshops/wkshp_2018_10.cfm
Learn more about our Mars 2020 rover HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.







Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий