
One hundred years ago, Einstein’s theory of general relativity was supported by the results of a solar eclipse experiment. Even before that, Einstein had developed the theory of special relativity — a way of understanding how light travels through space.
Particles of light — photons — travel through a vacuum at a constant pace of more than 670 million miles per hour.
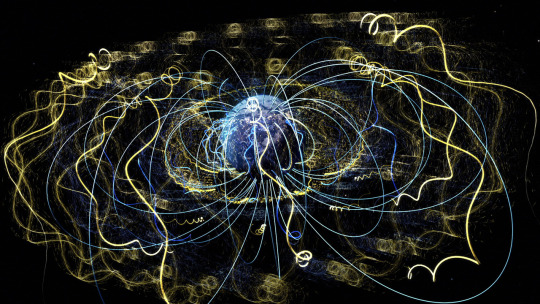
All across space, from black holes to our near-Earth environment, particles are being accelerated to incredible speeds — some even reaching 99.9% the speed of light! By studying these super fast particles, we can learn more about our galactic neighborhood.
Here are three ways particles can accelerate:
1) Electromagnetic Fields!
Electromagnetic fields are the same forces that keep magnets on your fridge! The two components — electric and magnetic fields — work together to whisk particles at super fast speeds throughout the universe. In the right conditions, electromagnetic fields can accelerate particles at near-light-speed.
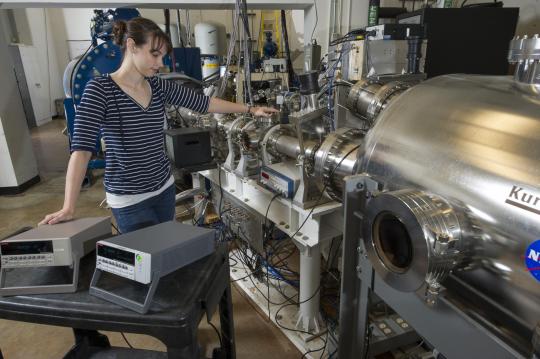
We can harness electric fields to accelerate particles to similar speeds on Earth! Particle accelerators, like the Large Hadron Collider and Fermilab, use pulsed electromagnetic fields to smash together particles and produce collisions with immense amounts of energy. These experiments help scientists understand the Big Bang and how it shaped the universe!
2) Magnetic Explosions!
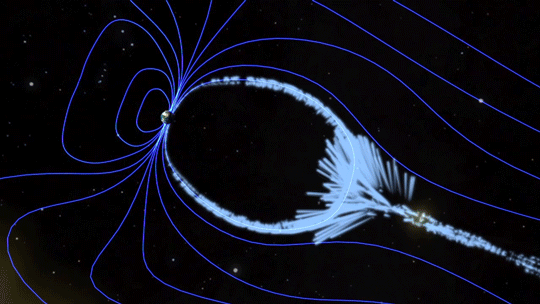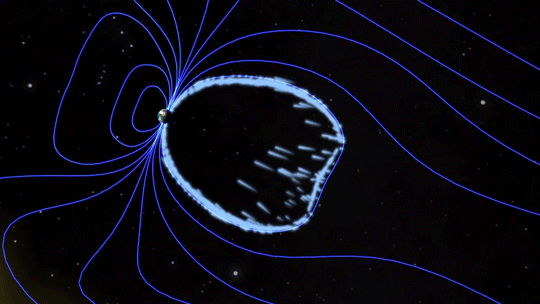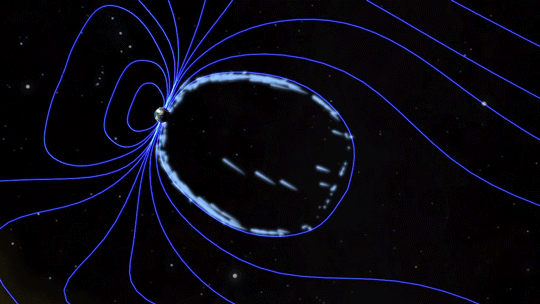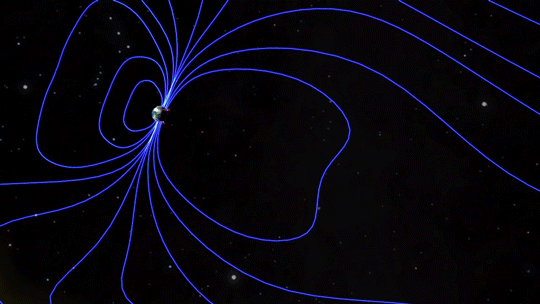
Magnetic fields are everywhere in space, encircling Earth and spanning the solar system. When these magnetic fields run into each other, they can become tangled. When the tension between the crossed lines becomes too great, the lines explosively snap and realign in a process known as magnetic reconnection. Scientists suspect this is one way that particles — for example, the solar wind, which is the constant stream of charged particles from the Sun — are sped up to super fast speeds.
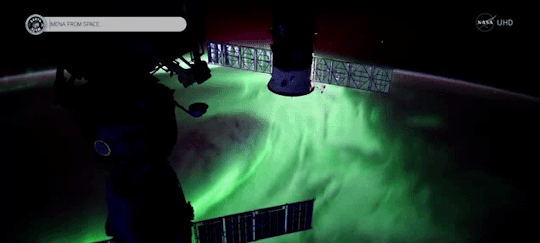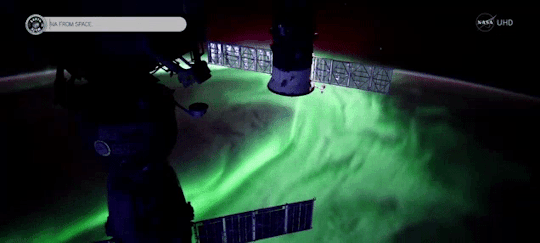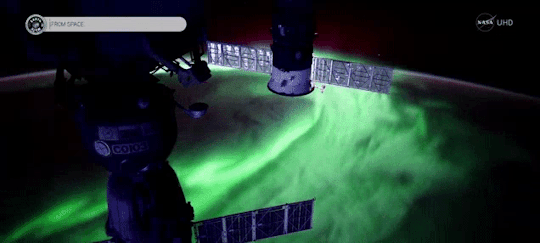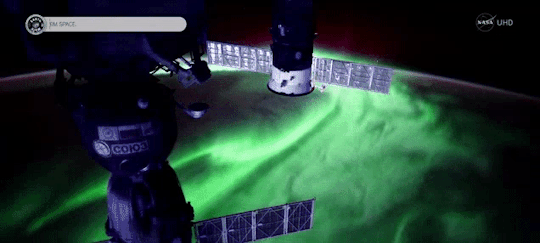
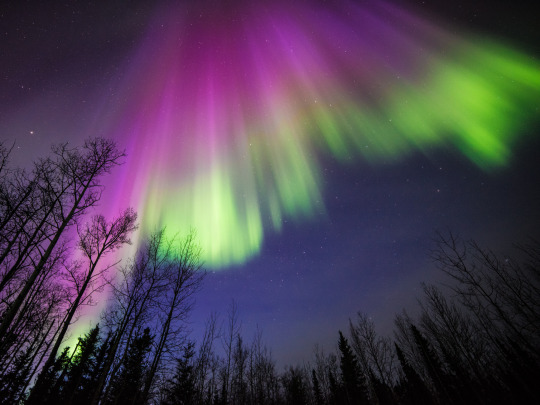
When magnetic reconnection occurs on the side of Earth facing away from the Sun, the particles can be hurled into Earth’s upper atmosphere where they spark the auroras.
3) Wave-Particle Interactions!
Particles can be accelerated by interactions with electromagnetic waves, called wave-particle interactions. When electromagnetic waves collide, their fields can become compressed. Charged particles bounce back and forth between the waves, like a ball bouncing between two merging walls. These types of interactions are constantly occurring in near-Earth space and are responsible for damaging electronics on spacecraft and satellites in space.

Wave-particle interactions might also be responsible for accelerating some cosmic rays from outside our solar system. After a supernova explosion, a hot, dense shell of compressed gas called a blast wave is ejected away from the stellar core. Wave-particle interactions in these bubbles can launch high-energy cosmic rays at 99.6% the speed of light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.





Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий