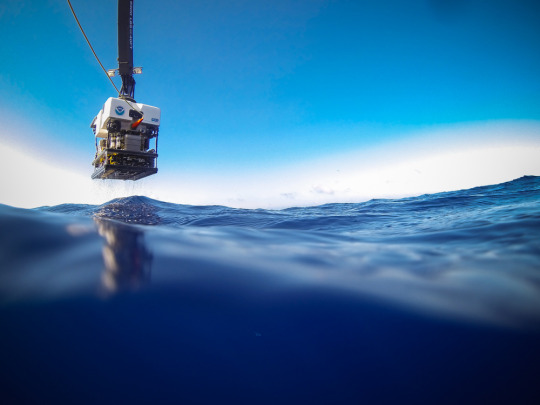

Image Credit: NOAA
Earth’s ocean has been the backdrop for ancient epics, tales of fictional fish and numerous scientific discoveries. It was, and will always be, a significant piece of the Earth’s story. Most of the ocean is unexplored– about 95% of this underwater realm is unseen by human eyes (NOAA). There is only one global Ocean. In fact, the ocean represents over 70% of the Earth’s surface and contains 96.5% of the Earth’s water.
We and the NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration and Research work together alongside organizations like the Schmidt Ocean Institute and Ocean Exploration Trust to better understand our oceans and its processes. While space may be the final frontier, understanding our own planet helps scientists as they explore space and study how our universe came to be.
On #WorldOceansDay let’s explore how Earth’s ocean informs our research throughout the solar system.
Earth and Exoplanets

“In interpreting what we see elsewhere in the solar system and universe, we always compare with phenomena that we already know of on Earth…We work from the familiar toward the unknown.” — Norman Kuring, NASA Goddard
We know of only one living planet: our own. As we move to the next stage in the search for alien life, the effort will require the expertise of scientists of all disciplines. However, the knowledge and tools NASA has developed to study life on Earth will also be one of the greatest assets to the quest.
The photo above shows what Earth would look like at a resolution of 3 pixels, the same that exoplanet-discovering missions would see. What should we look for, in the search of other planets like our own? What are the unmistakable signs of life, even if it comes in a form we don’t fully understand? Liquid water; every cell we know of – even bacteria around deep-sea vents that exist without sunlight – requires water.
Phytoplankton (Algae) Bloom vs. Atmosphere of Jupiter
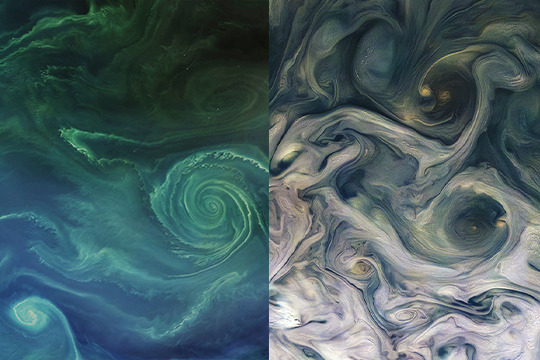
Jupiter’s storms are mesmerizing in their beauty, captured in many gorgeous photos throughout the decades from missions like Voyager 1 and Juno. The ethereal swirls of Jupiter are the result of fluids in motion on a rotating body, which might come as a surprise, since its atmosphere is made of gas!
The eddies in Jupiter’s clouds appear very similar to those found in Earth’s ocean, like in the phytoplankton (or algae) bloom in the Baltic Sea, pictured above. The bloom was swept up in a vortex, just a part of how the ocean moves heat, carbon, and nutrients around the planet. Blooms like this, however, are not all beauty — they create “dead zones” in the areas where they grow, blooming and decaying at such a high rate that they consume all the oxygen in the water around them.
Arctic Sea Ice and Europa Ice Crust

While the Arctic (North Pole) and the Antarctic (South Pole) are “polar opposites,” there is one huge difference between the North and South Poles– land mass. The Arctic is ocean surrounded by land, while the Antarctic is land surrounded by ocean. The North Pole is located in the middle of the Arctic Ocean amid waters that are almost permanently covered with constantly shifting sea ice.
By studying this sea ice, scientists can research its impact on Earth system and even formation processes on other bodies like Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter. For example, it is possible that the reddish surface features on Europa’s ice may have communicated with a global subsurface ocean layer during or after their formation.
Aquanauts and Astronauts
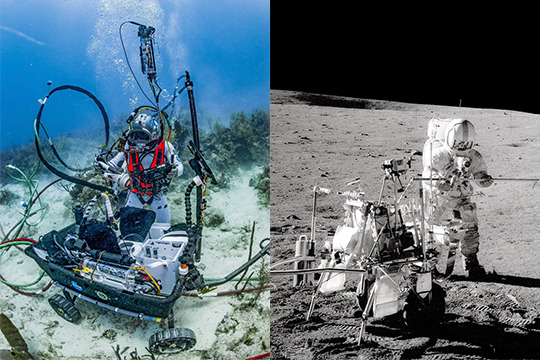
As new missions are being developed, scientists are using Earth as a testbed. Just as prototypes for our Mars rovers made their trial runs on Earth’s deserts, researchers are testing both hypotheses and technology on our oceans and extreme environments.
NEEMO, our Extreme Environment Mission Operations project, is an analog mission that sends groups of astronauts, engineers and scientists to live in Aquarius, the world’s only undersea research station located off the Florida Keys, 62 feet (19 meters) below the surface. Much like space, the undersea world is a hostile, alien place for humans to live. NEEMO crew members, known as aquanauts, experience some of the same challenges there that they would on a distant asteroid, planet or moon.
Deep-sea Robotic Exploration and Space Robotic Exploration

Video credit: Deep Sea Robotics/Schmidt Ocean Institute and Mars Curiosity rover/NASA
From mapping the seafloor through bathymetry to collecting samples on the surface of Mars, researchers are utilizing new technologies more than ever to explore. Satellite and robotic technology allow us to explore where humans may not be able to– yet. They teach us valuable lessons about the extreme and changing environments, science, as well as provide a platform to test new technologies.
Jezero Crater and Dvina River Delta, Arkhangelsk, Russia/Mars Delta
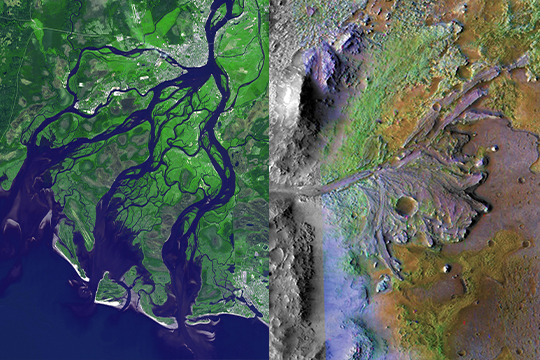
River deltas, the point where a river meets the ocean, are sites of rich sediment and incredible biodiversity. The nutrients that rivers carry to the coastlines make a fertile place for fish and shellfish to lay their eggs.
The Jezero crater on Mars (pictured in false-color on the right) has been selected as the Mars2020 landing site, and has a structure that looks much like a river delta here on Earth! Pictures from our Mars Global Surveyor orbiter show eroded ancient deposits of transported sediment long since hardened into interweaving, curved ridges of layered rock. This is one of many hints that Mars was once covered in an ancient ocean that had more water than the Arctic Ocean. Studying these deltas on Earth helps us spot them on other planets, and learning about the ocean that was once on Mars informs how our own formed.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.




Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий