Our Space Launch System rocket is on the move this summer — literally. With the help of big and small businesses in all 50 states, various pieces of hardware are making their way to Louisiana for manufacturing, to Alabama for testing, and to Florida for final assembly. All of that work brings us closer to the launch of Artemis 1, SLS and Orion’s first mission to the Moon.

By land and by sea and everywhere in between, here’s why our powerful SLS rocket is truly America’s rocket:
Rollin’ on the River

The SLS rocket will feature the largest core stage we have ever built before. It’s so large, in fact, that we had to modify and refurbish our barge Pegasus to accommodate the massive load. Pegasus was originally designed to transport the giant external tanks of the space shuttles on the 900-mile journey from our rocket factory, Michoud Assembly Facility, in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Now, our barge ferries test articles from Michoud along the river to Huntsville, Alabama, for testing at Marshall Space Flight Center. Just a week ago, the last of four structural test articles — the liquid oxygen tank — was loaded onto Pegasus to be delivered at Marshall for testing. Once testing is completed and the flight hardware is cleared for launch, Pegasus will again go to work — this time transporting the flight hardware along the Gulf Coast from New Orleans to Cape Canaveral.
Chuggin’ along

The massive, five-segment solid rocket boosters each weigh 1.6 million pounds. That’s the size of four blue whales! The only way to move the components for the powerful boosters on SLS from Promontory, Utah, to the Booster Fabrication Facility and Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy is by railway. That’s why you’ll find railway tracks leading from these assembly buildings and facilities to and from the launch pad, too. Altogether, we have about 38-mile industrial short track on Kennedy alone. Using a small fleet of specialized cars and hoppers and existing railways across the US, we can move the large, bulky equipment from the Southwest to Florida’s Space Coast. With all the motor segments complete in January, the last booster motor segment (pictured above) was moved to storage in Utah. Soon, trains will deliver all 10 segments to Kennedy to be stacked with the booster forward and aft skirts and prepared for flight.
It’s a bird, it’s a plane, no, it’s super Guppy!
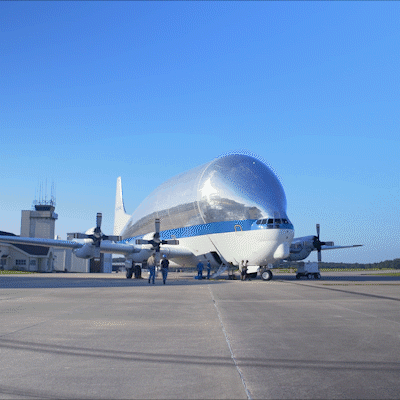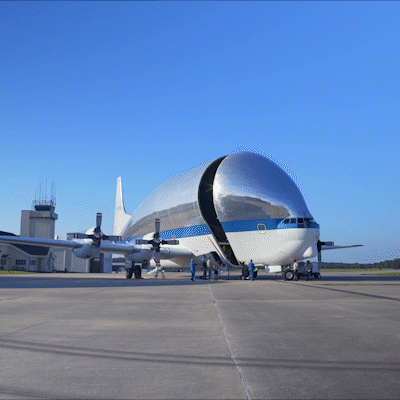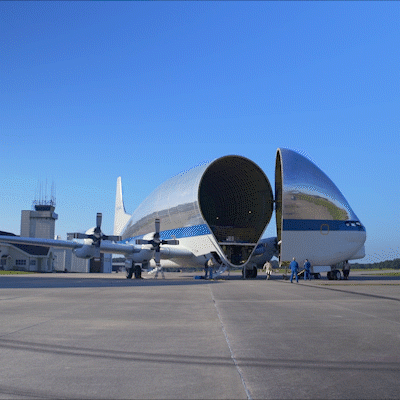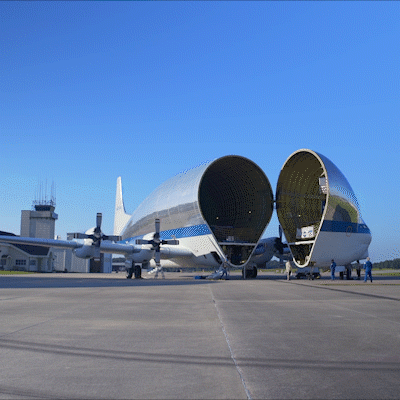
A regular passenger airplane doesn’t have the capacity to carry the specialized hardware for SLS and our Orion spacecraft. Equipped with a unique hinged nose that can open more than 200 degrees, our Super Guppy airplane is specially designed to carry the hulking hardware, like the Orion stage adapter, to the Cape. That hinged nose means cargo is actually loaded from the front, not the back, of the airplane. The Orion stage adapter, delivered to Kennedy in 2018, joins to the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage, which will give our spacecraft the push it needs to go to the Moon on Artemis 1. It fit perfectly inside the Guppy’s cargo compartment, which is 25 feet tall and 25 feet wide and 111 feet long.
All roads lead to Kennedy
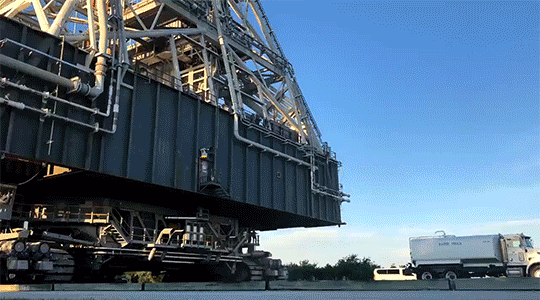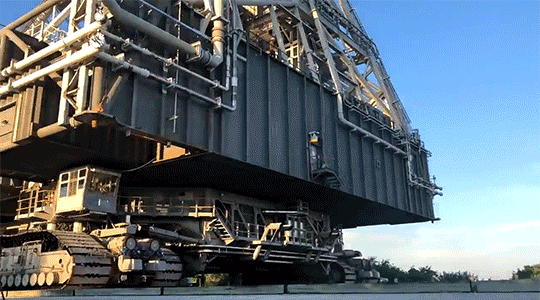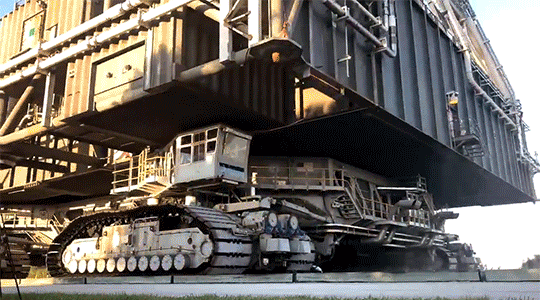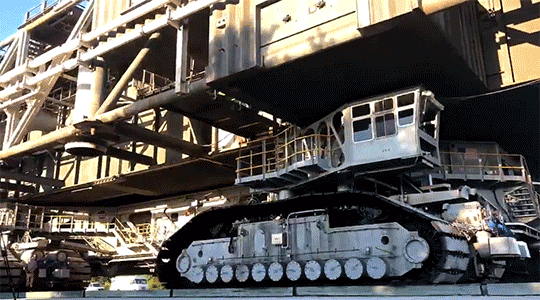
In the end, all roads lead to Kennedy, and the star of the transportation show is really the “crawler.” Rolling along at a delicate 1 MPH when it’s loaded with the mobile launcher, our two crawler-transporters are vital in bringing the fully assembled rocket to the launchpad for each Artemis mission. Each the size of a baseball field and powered by locomotive and large power generator engines, one crawler-transporter is able to carry 18 million pounds on the nine-mile journey to the launchpad. As of June 27, 2019, the mobile launcher atop crawler-transporter 2 made a successful final test roll to the launchpad, clearing the transporter and mobile launcher ready to carry SLS and Orion to the launchpad for Artemis 1.
Dream Team

It takes a lot of team work to launch Artemis 1. We are partnering with Boeing, Northrop Grumman and Aerojet Rocketdyne to produce the complex structures of the rocket. Every one of our centers and more than 1,200 companies across the United States support the development of the rocket that will launch Artemis 1 to the Moon and, ultimately, to Mars. From supplying key tools to accelerate the development of the core stage to aiding the transportation of the rocket closer to the launchpad, companies like Futuramic in Michigan and Major Tool & Machine in Indiana, are playing a vital role in returning American astronauts to the Moon. This time, to stay. To stay up to date with the latest SLS progress, click here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.








Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий